WHAT IS VITAMIN B12 GOOD FOR?
Vitamin B12, also known as cobalamin, is arguably the most important of the eight B vitamins and is an often-overlooked vitamin which is essential to keep our brains sharp, our mood in check and our nervous system firing on all cylinders. It is also needed to form DNA and healthy red blood cells.
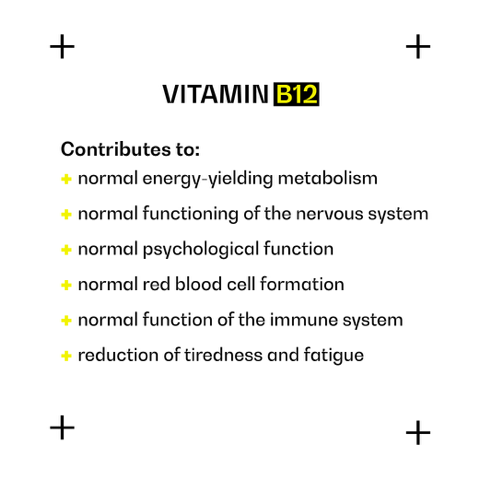
Vitamin B12 supports your health by contributing to:
- normal energy-yielding metabolism
- normal red blood cell formation
- the reduction of tiredness and fatigue
- normal functioning of the nervous system
- normal psychological function
- normal function of the immune system
- normal homocysteine metabolism
Vitamin B12 also has a role in the process of cell division.
Because vitamin B12 is a water-soluble vitamin, it cannot be stored in the body and must be obtained daily from diet or supplements.
Good sources of vitamin B12 are beef, pork, fish, milk, cheese and eggs.
If you're vegetarian or vegan, you may not get enough B12 from your diet putting you at risk of deficiency.
In you are taking taking metformin, a widely used treatment for type 2 diabetes, you're also at risk of vitamin B12 deficiency, per the warning issued by the MHRA.
However, it is not just vegans and those on metformin who should worry about their B12 levels. Millions of others are at risk too. Could you be one of them?
SYMPTOMS OF B12 DEFICIENCY
Symptoms of deficiency include anaemia, fatigue, muscle weakness, depression, disturbed vision, and dementia.
Those at risk of vitamin B12 deficiency include: older adults (as we get older we are less able to absorb B12 effectively); people on a strict vegan diet; people with gastrointestinal disorders, such as Crohn’s disease or celiac disease; those who have had gastrointestinal surgeries, such as bariatric surgery or bowel resection surgery; and those who take metformin for blood sugar control.
If a vitamin B12 deficiency is left unchecked, you could develop megaloblastic anaemia, a condition in which the bone marrow produces abnormally large red blood cells. The abnormal cells are so large they often can’t get out of your bone marrow to move into your bloodstream to carry oxygen from your lungs to your tissues and back again.
A B12 deficiency can also affect fertility and in extreme cases it has been linked to nerve damage and cardiovascular disease.
It’s worth speaking to your doctor if you’re concerned about the amount of vitamin B12 in your diet, or your body’s ability to absorb it.

SCIENTIFIC BENEFITS OF VITAMIN B12
Vitamin B12 plays key roles in converting food into energy, fighting fatigue, keeping the brain and nervous system functioning properly, regulating our immune system and mood, and controlling levels of the amino acid homocysteine, elevated levels of which are associated with numerous diseases. Researchers have also found a link between B12 deficiency and male sexual function.
Let's delve into some of the science below:
IMPROVES MOOD AND SYMPTOMS OF DEPRESSION
Vitamin B12 contributes to normal psychological function and is needed for the production of serotonin, a chemical responsible for regulating mood. Therefore, vitamin B12 deficiency may lead to decreased serotonin production, which may cause a depressed mood. Studies support the use of vitamin B12 supplements for improving symptoms of depression in people with a vitamin B12 deficiency. For example:
+ A controlled study in people with depression and low vitamin B12 levels found that those who received both antidepressants and vitamin B12 were more likely to show improved depressive symptoms, compared to those treated with antidepressants alone.
+ A study discovered that vitamin B12 deficiency was associated with twice the risk of severe depression.
+ A study involving 3884 elderly people with depressive disorders found that those with vitamin B12 deficiency were almost 70% more likely to experience depression than those with normal vitamin B12 status.
+ A review of studies concluded that supplementation of Vitamin B12 early enough can delay the onset of depression.
MAINTAINS BRAIN FUNCTION
The body needs vitamin B12 for neurological and psychological function, so it comes as no surprise that Vitamin B12 deficiency has been associated with memory loss, especially in older adults. For example:
+ A study in people with early-stage dementia showed that a combination of vitamin B12 and omega-3 fatty acid supplements slowed mental decline.
+ A study found that even vitamin B12 levels on the low side of normal can contribute to poor memory performance.
+ A study involving 202 patients with minimal cognitive impairment found that 84% reported marked symptomatic improvement after B12 replacement.
+ A study involving 3136 adults followed for 20 years from age 18 to 30, found that that those in the highest quintile of dietary vitamin B12 intake at baseline (median 8.7 µg/day) had better psychomotor speed 20 to 25 years later versus those with the lowest dietary intake of B12 (median 2.2 µg/day).
+ A study using functional biomarkers of vitamin B12 status showed a trend towards associations between poor vitamin B12 status in an ageing population and faster cognitive decline and risk of Alzheimer’s disease.
SUPPORTS SEXUAL FUNCTION
Research has shown that when our body lacks enough B12, testosterone levels can drop significantly and that vitamin B12 also impacts testicular health and sperm quality, as well as energy levels and stamina. For example:
+ A clinical study found that 76% of men presenting with chronic testicular pain were deemed deficient for testosterone and B12 levels. Of those that elected to receive B12 and/or testosterone replacement 65% reported significant improvement of symptoms.
+ A meta-analysis concluded that mainstream published work demonstrates the positive effects of vitamin B12 on semen quality: first, by increasing sperm count, and by enhancing sperm motility and reducing sperm DNA damage.
Furthermore, researchers believe vitamin B12 supplements may improve erectile function. This is because vitamin B12 is involved in the breakdown of homocysteine – an amino acid which can damage artery linings when allowed to build up in the circulation. Hardening and furring up of the arteries (atherosclerosis) is a leading cause of erectile difficulties in older males and in those with diabetes. For example:
+ A systemic review and meta-analysis of nine studies including 1,320 men found that the men with erectile dysfunction (ED) were approximately twice as likely to have elevated levels of homocysteine.
+ A study involving 691 men who identified as having erectile dysfunction (ED), found that age, homocysteine (Hcy) and vitamin B12 levels were the main determinants in ED. Hcy levels were increased in men over 45 with ED, but vitamin B12 was decreased in men under 45 with ED.
GIVES YOU AN ENERGY BOOST
Vitamin B12 supplements have long been touted as the go-to product for a surge of energy. This is because one of the most common early signs of vitamin B12 deficiency is fatigue or lack of energy. Vitamin B12 helps maintain our energy levels by contributing to energy-yielding metabolism and red blood cell formation. For example:
+ Research shows that B12, along with all the other B vitamins, is involved in the production of energy. In fact, one of the most common early signs of vitamin B12 deficiency is fatigue or lack of energy.
+ Research shows B12 is vital for normal red blood cell formation which is critical for efficiently transporting oxygen throughout the body, and a chronic deficiency in vitamin B12 can trigger anaemia, symptoms of which include fatigue and weakness.
+ A study showed that deficiencies in B12 can result in diminished energy and exercise tolerance, together with fatigue and shortness of breath. These hematologic symptoms regress and disappear with B12 supplementation.
HELPS PREVENT ANAEMIA
Vitamin B12 plays a vital role in helping your body produce red blood cells. A deficiency in B12 can lead to Anaemia. This is where your body produces a lower-than-normal amount of healthy red blood cells, and you may experience symptoms such as extreme tiredness, a lack of energy, feeling faint, a pale yellow tinge to your skin and/or a sore red tongue. Studies have shown that among patients with anaemia up to 20% were due to a B12 deficiency.
MAINTAINS HEALTHY HAIR, SKIN AND NAILS
Adequate levels of Vitamin B12 are needed to promote healthy hair, skin and nails given its role in cell production. In fact, low vitamin B12 levels can cause various dermatologic symptoms, including hyperpigmentation, acne, hair changes, nail discolouration, vitiligo and angular stomatitis (inflamed and cracked mouth corners).
SUPPORTS BONE HEALTH
Low blood levels of vitamin B12 have been associated with an increased risk of osteoporosis. One study in more than 2,500 adults showed that people with a vitamin B12 deficiency also had lower than normal bone mineral density which can become delicate and fragile over time, leading to an increased risk of osteoporosis.
REDUCES RISK OF DISEASE
Vitamin B12 is vital for proper functioning of the immune system and a cofactor in controlling levels of the amino acid homocysteine. Studies show that a deficiency in B12 and/or elevated levels of homocysteine has been associated with many diseases. For example:
+ Evidence shows a deficiency in B12 can lead to an increased risk of hyperhomocysteinemia (elevated levels of homocysteine in the blood) which has been regarded as a marker of cardiovascular disease and a definite risk factor for many other diseases, including neurodegenerative diseases, auto immune disorders, diabetes, osteoporosis, age-related macular degeneration and cancer.
+ A controlled study showed that vitamin B12 helps decrease homocysteine levels, a type of amino acid that is associated with an increased risk of stroke.
+ A meta-analysis found that supplementing vitamin B12 may lower homocysteine levels which has been associated with an increased risk of age-related macular degeneration (an eye disease that mainly affects central vision).
+ A review concluded that disturbed homocysteine metabolism is associated with many forms of human cancer.
+ A review of 9 studies, found that researchers reported deficiency in B12 was associated with viral diseases.
+ A comprehensive review of evidence found that the consumption of a healthy diet containing vitamin B12 sources, and especially supplementation with methylcobalamin and cyanocobalamin, are promising alternatives as adjuvants in the treatment of COVID-19, especially in patients with B12 deficiency or deficiency risk.
Vitamin B12 is vital to your health and deficiency can occur if your diet lacks adequate amounts of it or your body is unable to fully absorb it from the food you eat.
HIMMENSE supplements contain Vitamin B12.
Research is for information only and should not replace medical care. Consult a doctor or healthcare professional if you have any questions or are taking any other medications before you try any supplements.
Read more Men's Health & Lifestyle blogs from HIMMENSE here



